Back to Blogs
Back to Blogs
Announcing Ballerina Swan Lake Update 9 (2201.9.0)
Ballerina Team
27 May 2024
We are excited to announce the Ballerina Swan Lake Update 9 (2201.9.0) release, which adds new features and improvements to many areas, including data-mapping, JSON, XML, and SOAP handling, crypto, and build process as described below.
AI-assisted data mapping
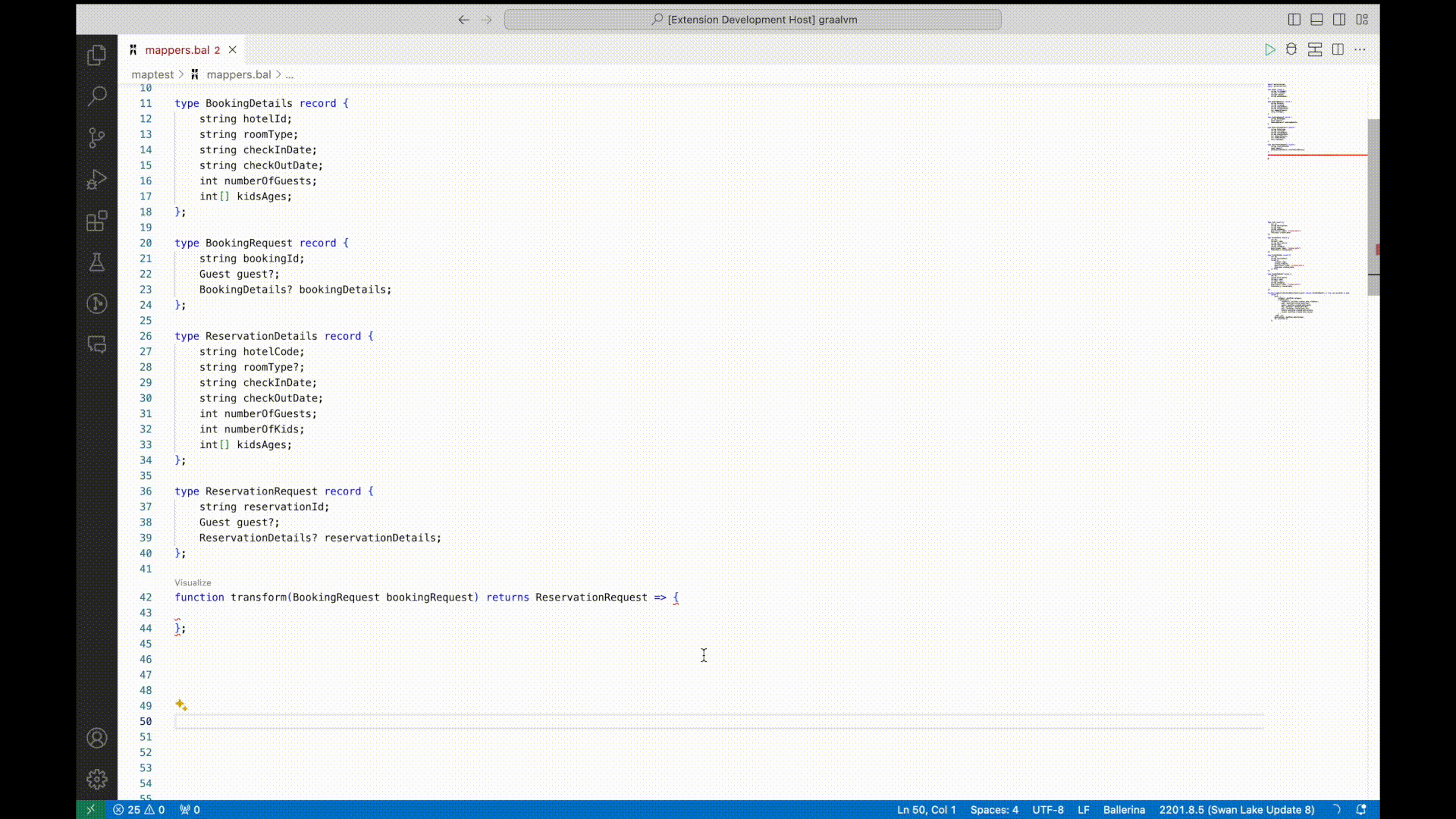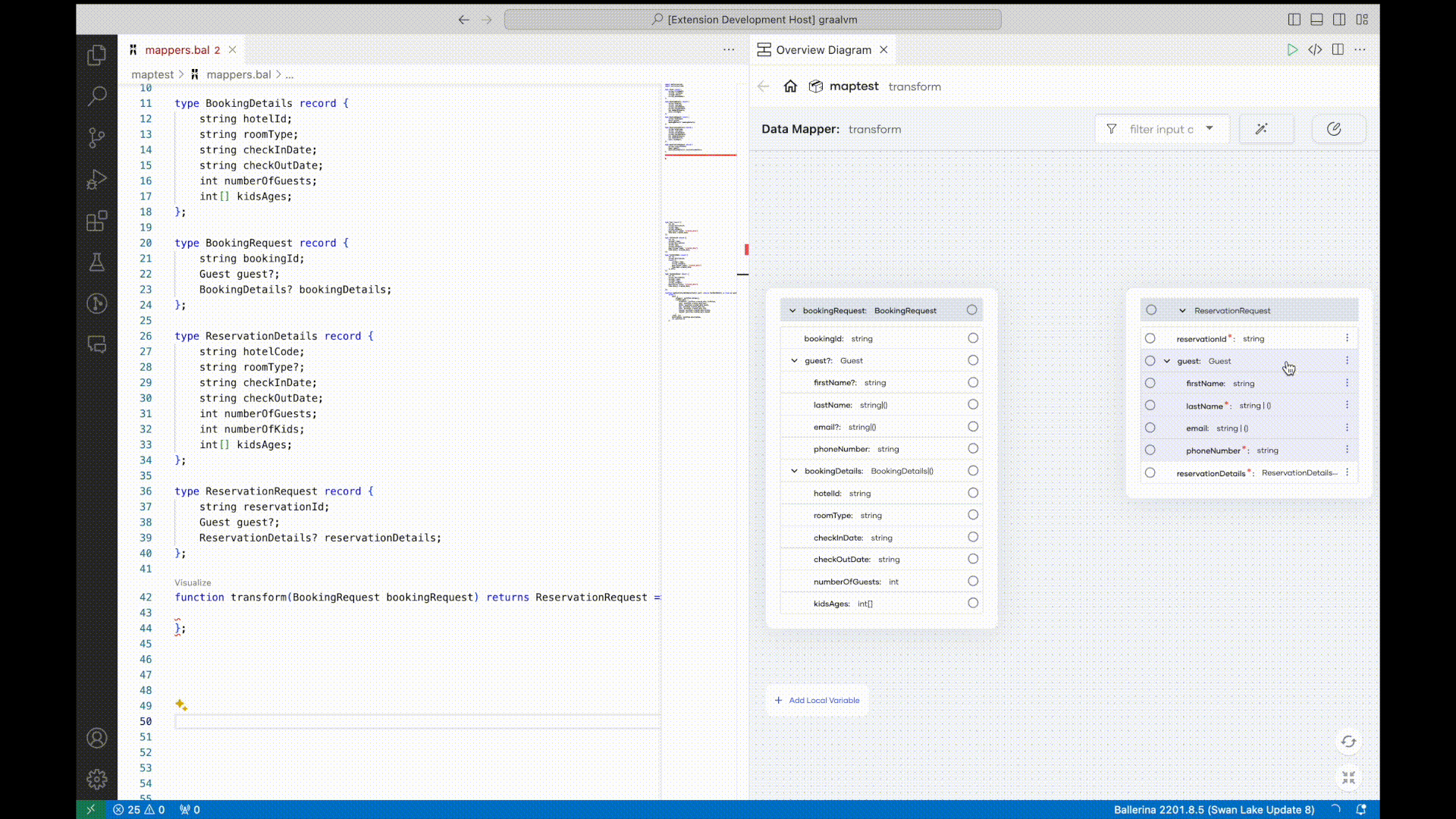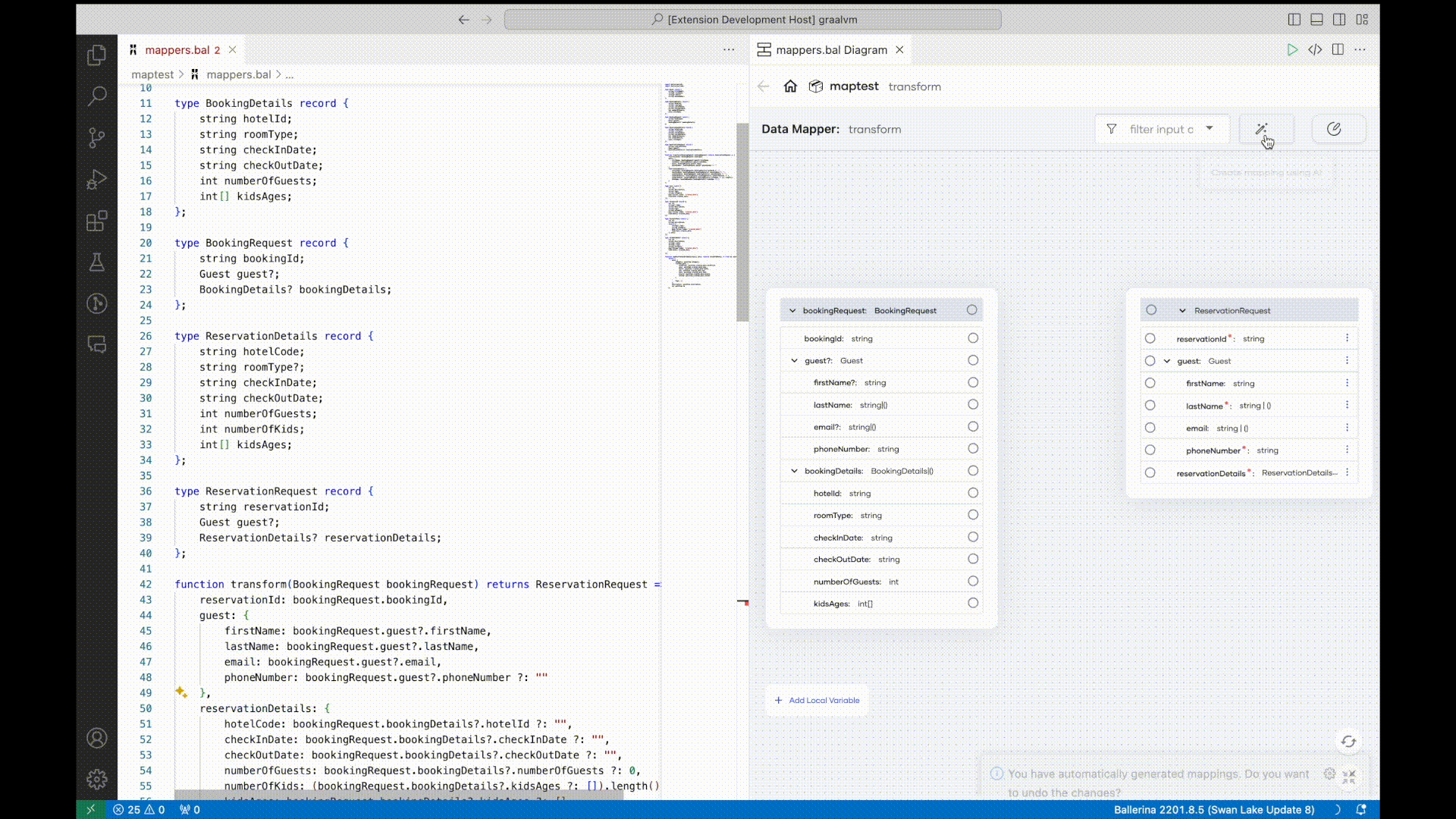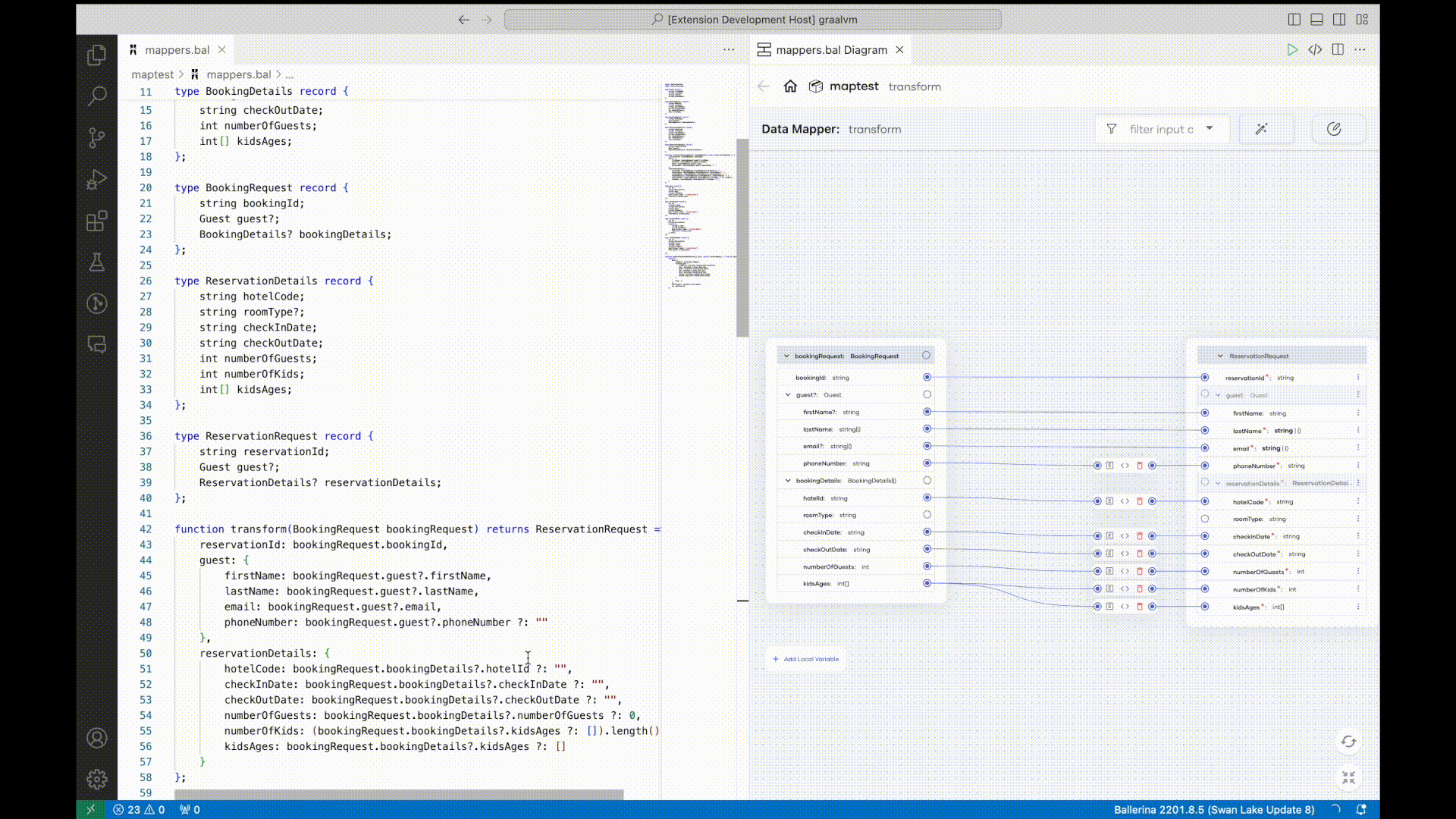
Data mapping is a frequent but time-consuming task in integrations due to the number of mappings required for a typical integration project and the complexity of those mappings. In order to simplify this process, this Ballerina release introduces AI-assisted data mappings. Integration developers can select input and output data records and trigger the AI-assisted data mapping feature, which automatically maps fields using OpenAI. Once the AI-based mapping is completed, developers can manually update mappings if necessary.
For more information, see automated data mapper.
Quantum-safe crypto algorithms
As an integration language, data security is a main priority of Ballerina. Therefore, in order to overcome possible weaknesses of traditional crypto algorithms against quantum computing, Ballerina adds support for quantum-safe crypto algorithms from this release. With this functionality, Ballerina programs can now use crypto algorithms such as ML-KEM-768, RSA-KEM-ML-KEM-768, and ML-DSA65 to encrypt and sign data.
See Ballerina crypto package for more information.
Improved JSON and XML handling
With this release, it is possible to navigate JSON data in Ballerina using JSONPath expressions. Complex data retrievals can be performed within the Ballerina code using this feature as follows:
// Use a JSONPath expression to extract the list of titles in the books array. json titles = check jsondata:read(books, `$..title`); io:println(titles); // Use a JSONPath expression to extract the list of published years for the // books that have a price value of more than 80. json years = check jsondata:read(books, `$..[?(@.price > 80)].year`); io:println(years); // Use a JSONPath expression to extract the total sum of the prices of the books. json sum = check jsondata:read(books, `$..price.sum()`); io:println(sum);
In addition, the data projection feature enables the conversion of JSON or XML data into Ballerina records by specifying only the required fields from the source data. This is useful for extracting only the required information from very large JSON or XML messages, which are common in interactions with B2B and enterprise applications.
See JSONPath and JSON data projection examples.
SOAP support
This release introduces support for invoking SOAP 1.1 and 1.2 endpoints with web services security policies. This enables Ballerina programs to communicate securely with SOAP services and, for example, expose SOAP services as REST endpoints.
For more details, see SOAP client examples.
Support for integrating code generation tools with the build process
Many integration technologies, such as OpenAPI, gRPC, data access, and EDI, rely on code generation from schemas. For example, when using Ballerina in an OpenAPI project, developers usually generate REST clients and records from the OpenAPI schema and then write the rest of the Ballerina code by using the generated code.
The problem with this approach is that developers either have to store the generated code in a version control system, or they have to manually generate code each time before a build. With this release, Ballerina developers can overcome this problem by using the code generation capabilities integrated with the build process. Information required for code generation can be specified in the Ballerina.toml file.
See automated client generation in OpenAPI tool for an example usage.
Bal persist - Ballerina record generation from database schemas
Bal persist greatly simplifies interactions with data stores by allowing Ballerina developers to work with usual Ballerina records for data access. However, in previous versions, developers had to start from Ballerina records and generate the data schema from that. With this release, the bal persist tool can introspect existing data schemas and generate Ballerina records to work with those schemas. This makes the bal persist applicable in almost all data access scenarios, whether starting with a new database or working with an existing one.
See database introspection for more information.
See the release note for a comprehensive overview of Swan Lake Update 9's new features and improvements. We encourage our community to explore these features and provide feedback. Your input is invaluable in shaping the future of Ballerina and ensuring it meets your needs.
Cheers to the Ballerina community and the bright future of it!